Exhibit 99.1
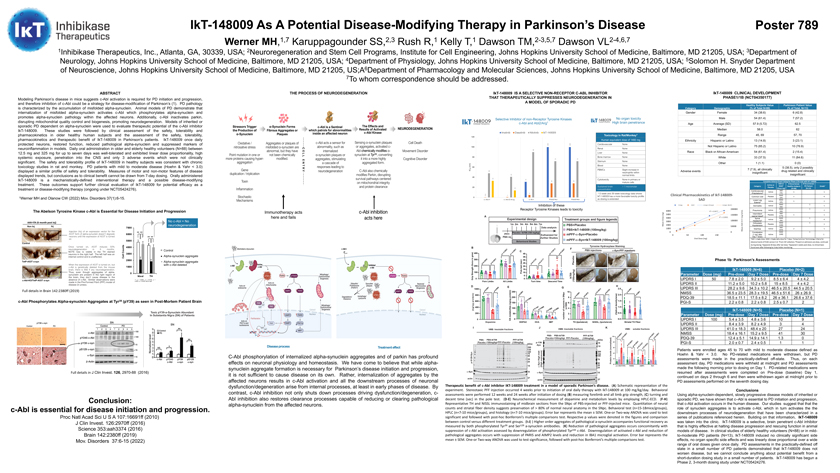
IkT-148009 As A Potential Disease-Modifying Therapy in Parkinson’s Disease Poster 789 Werner MH,1,7 Karuppagounder SS,2,3 Rush R,1 Kelly T,1 Dawson TM,2-3,5,7 Dawson VL2-4,6,7 1Inhibikase Therapeutics, Inc., Atlanta, GA, 30339, USA; 2Neuroregeneration and Stem Cell Programs, Institute for Cell Engineering, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD 21205, USA; 3Department of Neurology, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD 21205, USA; 4Department of Physiology, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD 21205, USA; 5Solomon H. Snyder Department of Neuroscience, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD 21205, US;A6Department of Pharmacology and Molecular Sciences, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD 21205, USA 7To whom correspondence should be addressed. ABSTRACT Modeling Parkinson’s disease in mice suggests c-Abl activation is required for PD initiation and progression, and therefore inhibition of c-Abl could be a strategy for disease-modification of Parkinson’s (1). PD pathology is characterized by the accumulation of misfolded alpha-synuclein. Animal models of PD demonstrate that internalization of misfolded alpha-synuclein activates c-Abl which phosphorylates alpha-synuclein and promotes alpha-synuclein pathology within the affected neurons. Additionally, c-Abl inactivates parkin, disrupting mitochondrial quality control and biogenesis, promoting neurodegeneration. Models of inherited or sporadic PD dependent on alpha-synuclein were used to evaluate therapeutic potential of the c-Abl inhibitor IkT-148009. These studies were followed by clinical assessment of the safety, tolerability and pharmacokinetics in older healthy human subjects and the assessment of the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics and therapeutic benefit of IkT-148009 in Parkinson’s patients. IkT-148009 once daily protected neurons, restored function, reduced pathological alpha-synuclein and suppressed markers of neuroinflammation in models. Daily oral administration in older and elderly healthy volunteers (N=88) between 12.5 mg and 325 mg for up to seven days was well-tolerated and exhibited linear dose proportionality, high systemic exposure, penetration into the CNS and only 3 adverse events which were not clinically significant. The safety and tolerability profile of IkT-148009 in healthy subjects was consistent with chronic toxicology studies in rat and monkey. PD patients with mild to moderate disease (Hoehn & Yahr < 3.0) displayed a similar profile of safety and tolerability. Measures of motor and non-motor features of disease displayed trends, but conclusions as to clinical benefit cannot be drawn from 7-day dosing. Orally administered IkT-148009 is a mechanistically-defined interventional therapy and a possible disease-modifying treatment. These outcomes support further clinical evaluation of IkT-148009 for potential efficacy as a treatment or disease-modifying therapy (ongoing under NCT05424276). 1Werner MH and Olanow CW (2022) Mov. Disorders 37(1):6-15. The Abelson Tyrosine Kinase c-Abl is Essential for Disease Initiation and Progression No c-Abl = No neurodegeneration Injection (Inj) of an expression vector for the A53T form of alpha-synuclein doesn’t degrade neurons until the expression of A53T is turned on Once turned on, A53T induces 50% neurodegeneration in 6 months. Control NOTE loss is visible in the TH stained neurons in the right half. The left half was an internal control and is unaffected. Alpha-synuclein aggregate Alpha-synuclein aggregate When the expression of A53T is turned on, but with c-Abl deleted c-Abl is genetically deleted from the mouse brain, there is little if any neurodegeneration. Thus, even though aggregates of alpha-synucleiln are present in the right region of the brain, they don’t cause disease in the absence of c-Abl. Similar observations were **: p < 0.0001, p = 0.0154, p = made in the Pre-Formed Fibril (PFF) model of 0.0001, p = 0.0225, left-to-right disease (in press). Full details in Brain 142:2380ff (2019) c-Abl Phosphorylates Alpha-synuclein Aggregates at Tyr39 (pY39) as seen in Post-Mortem Patient Brain Toxic pY39-a-Synuclein Abundant In Substantia Nigra (SN) of Patients Full details in J Clin Invest. 126, 2970-88 (2016) Conclusion: c-Abl is essential for disease initiation and progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:16691ff (2010) J Clin Invest. 126:2970ff (2016) Science 353:aah3374 (2016) Brain 142:2380ff (2019) Mov. Disorders 37:6-15 (2022) THE PROCESS OF NEURODEGENERATION Immunotherapy acts here and fails Disease process Treatmenteffect C-Abl phosphorylation of internalized alpha-synuclein aggregates and of parkin has profound effects on neuronal physiology and homeostasis. We have come to believe that while alpha-synuclein aggregate formation is necessary for Parkinson’s disease initiation and progression, it is not sufficient to cause disease on its own. Rather, internalization of aggregates by the affected neurons results in c-Abl activation and all the downstream processes of neuronal dysfunction/degeneration arise from internal processes, at least in early phases of disease. By contrast, c-Abl inhibition not only shuts down processes driving dysfunction/degeneration, cAbl inhibition also restores clearance processes capable of reducing or clearing pathological alpha-synuclein from the affected neurons. IkT-148009 IS A SELECTIVE NON-RECEPTOR C-ABL INHIBITOR THAT THERAPEUTICALLY SUPPRESSES NEURODEGENERATION IN A MODEL OF SPORADIC PD Selective Inhibitor of non-Receptor Tyrosine Kinases No organ toxicity c-Abl and Abl2/Arg1 High brain penetrance Imatinib Dasatinib Nilotinib IkT-148009 Toxicology in Rat/Monkey1 120 Human equivalent dose of 1460 mg 100 100 Cardiovascular None 100 Renal None 90 Liver None 80 Bone marrow None 72 72 Sternum None (nm) Blood None 50 60 IC PBMCs Slight increase in 48 neutrophils within 41 normal limits 40 33 31 Cytotoxicity None in primary or 28 28 mature cells 20 Sustained brain > 1 micromolar 14 concentration 5 113 week and 39 week toxicology data shows . 6 0 1 IkT-148009 has a more favorable toxicity profile 0 c - Abl1 c - Abl2/Ar g c - Kit PDGFRa PDGFRb as dosing is extended Inhibition of these Receptor Tyrosine Kinases leads to toxicity 6000 (ng) 5000 Cmax 4000 3000 Mean 2000 1000 0 Therapeutic benefit of c-Abl inhibitor IKT-148009 treatment in a model of sporadic Parkinson’s disease. (A) Schematic representation of the experiment. Stereotaxic PFF injection occurred 4 weeks prior to initiation of oral daily therapy with IkT-148009 at 100 mg/kg/day. Behavioral assessments were performed 12 weeks and 24 weeks after initiation of dosing (B) measuring forelimb and all limb grip strength, (C) turning and decent time (sec) in the pole test. (D-E) Neurochemical measurement of dopamine and metabolism levels by employing HPLC-ECD. (F-H) Representative TH and NISSL immunostaining of midbrain sections from the SNpc of PBS-injected or PFF-injected mice. Quantitation of neural counts and striatal fiber density suggests preservation of > 80% of normal neural anatomy in the SNpc. Behavioral test (n=15-18mice/groups), HPLC (n=7-10 mice/groups), and histology (n=7-10 mice/groups). Error bar represents the mean ± SEM. One-or Two-way ANOVA was used to test significant and followed with post-hoc Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test. Respective p values were denoted in the figures and comparison between control versus different treatment groups. (I-J) ) Higher order aggregates of pathological a-synuclein accompanies functional recovery as measured by both phosphorylated Tyr39 and Ser129 a-synuclein antibodies. (K) Reduction of pathological aggregates occurs concomitantly with suppression of c-Abl activation assessed by downregulation of phosphorylated Tyr245 c-Abl. Downregulation of activated c-Abl and reduction of pathological aggregates occurs with suppression of PARIS and AIMP2 levels and reduction in IBA1 microglial activation. Error bar represents the mean ± SEM. One-or Two-way ANOVA was used to test significance, followed with post-hoc Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test. IkT-148009 CLINICAL DEVELOPMENT PHASE1/1B (NCT04350177) Healthy Subjects Value Parkinson Patient Value Category Demographic (% of Total N=88) (% of Total, N=13) Gender Female 34 (38.6) 6 (42.8) Male 54 (61.4) 7 (57.2) Age Average (SD) 57.9 (5.72) 62.5 Median 58.0 62 Range 45, 69 57, 70 Ethnicity Hispanic or Latino 13 (14.8) 3 (23.1) Not Hispanic or Latino 75 (85.2) 10 (76.9) Race Black or African American 54 (61.4) 2 (15.4) White 33 (37.5) 11 (84.6) Other 1 (1.1) 0 (0) 7 (7.9), all clinically 5 (38.5), only 2 possibly Adverse events drug related and clinically insignificant insignificant Complete Adverse Event Listing for Phase 1/1b trial with IkT-148009 Active or SAD or # Occurrences # Occurrences Category MAD(1) Healthy Subjects PD Patient Grade(2) Placebo (Dose mg) (N=88) (N=14) Cardiovascular SAD Active 1 1 (Palpitations)(6) (75) MAD Common cold Placebo 1 0 (25) Lower Leg MAD Active 1 1 Edema(5) (25) MAD 1 Dermatitis Active 1 (50) MAD 1 Pneumonia Active 1 (50) Intermittent SAD Placebo 1 1 vaginal bleed(4) (175) Spinal MAD 1 Active 0 Headache(3) (50) Orthostatic MAD 1 Placebo 1 Hypotension (100) SAD Diarrhea Active (325) 2 1 Constipation MAD 1 (1 day after Active (100) 1 Day 7 dose) (1)SAD = single dose, MAD = Single daily dose for 7 days; (2)Using Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) version 5.0; (3)From CSF collection; (4)Present on admission pre-dose, continued during dosing; (5)Appeared 28 days after last dose; (6)Appeared 2 weeks post-dose, no clinical basis found even after following by 3-day Holter monitoring. Phase 1b Parkinson’s Assessments IkT-148009 (N=6) Placebo (N=2) Parameter Dose (mg) Pre-dose Day 7 Dose Pre-dose Day 7 Dose UPDRS I 50 7.8 ± 2.0 9.2 ± 5.0 8.5 ± 6.4 4 ± 4.2 UPDRS II 11.2 ± 5.0 10.2 ± 5.8 15 ± 8.5 4 ± 4.2 UPDRS III 28.2 ± 9.6 34.3 ± 10.2 46.5 ± 20.5 44.5 ± 20.5 NMSS 36.5 ± 23.5 28.3 ± 19.5 46.5 ± 51.6 26 ± 26.9 PDQ-39 18.5 ± 11.1 17.5 ± 8.2 26 ± 36.1 26.6 ± 37.6 PGI-S 2.2 ± 0.8 2.2 ± 0.8 2.5 ± 0.7 2 IkT-148009 (N=5) Placebo (N=1) Parameter Dose (mg) Pre-dose Day 7 Dose Pre-dose Day 7 Dose UPDRS I 100 5.4 ± 3.5 4.8 ± 3.6 10 9 UPDRS II 8.4 ± 3.9 8.2 ± 4.9 3 4 UPDRS III 41.0 ± 18.3 48.4 ± 20 27 24 NMSS 18.4 ± 16.1 15.2 ± 9.5 41 30 PDQ-39 12.4 ± 5.1 14.9 ± 14.1 1.3 0 PGI-S 2.0 ± 0.7 2.4 ± 0.5 1 1 Patients were enrolled ages 45 to 70 with mild to moderate disease defined as Hoehn & Yahr < 3.0. No PD-related medications were withdrawn, but PD assessments were made in the practically-defined off-state. Thus, on each assessment day, PD medications were withheld at midnight and PD assessments made the following morning prior to dosing on Day 1. PD-related medications were resumed after assessments were completed on Pre-dose (baseline) Day 1, continued on days 2 through 6 and then were withdrawn again at midnight prior to PD assessments performed on the seventh dosing day. Conclusions Using alpha-synuclein-dependent, slowly progressive disease models of inherited or sporadic PD, we have shown that c–Abl is essential to PD initiation and progression, that c-Abl activation occurs in the human disease. Our studies suggest that that the role of synuclein aggregates is to activate c-Abl, which in turn activates the the downstream processes of neurodegeneration that have been characterized in a series of publications referenced herein. Building on that information, IkT-148009 was taken into the clinic. IkT-148009 is a selective, brain penetrant c-Abl inhibitor that is highly effective at halting disease progression and rescuing function in animal models of disease. In clinical studies of elderly healthy volunteers (N=88) or in mild-to-moderate PD patients (N=13), IkT-148009 induced no clinically significant side effects, no organ specific side effects and was linearly dose proportional over a wide range of oral doses given once daily. PD assessments in the practically-defined off state in a small number of PD patients demonstrated that IkT-148009 does not worsen disease, but we cannot conclude anything about potential benefit from a short-duration dosing study in a small number of patients. IkT-148009 has begun a Phase 2, 3-month dosing study under NCT05424276.